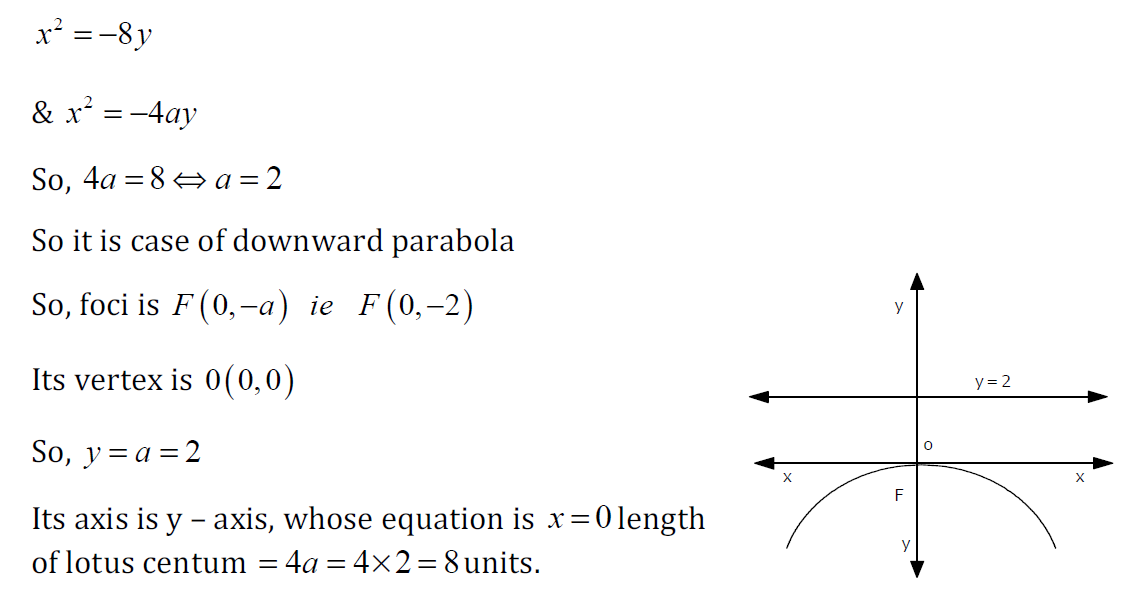
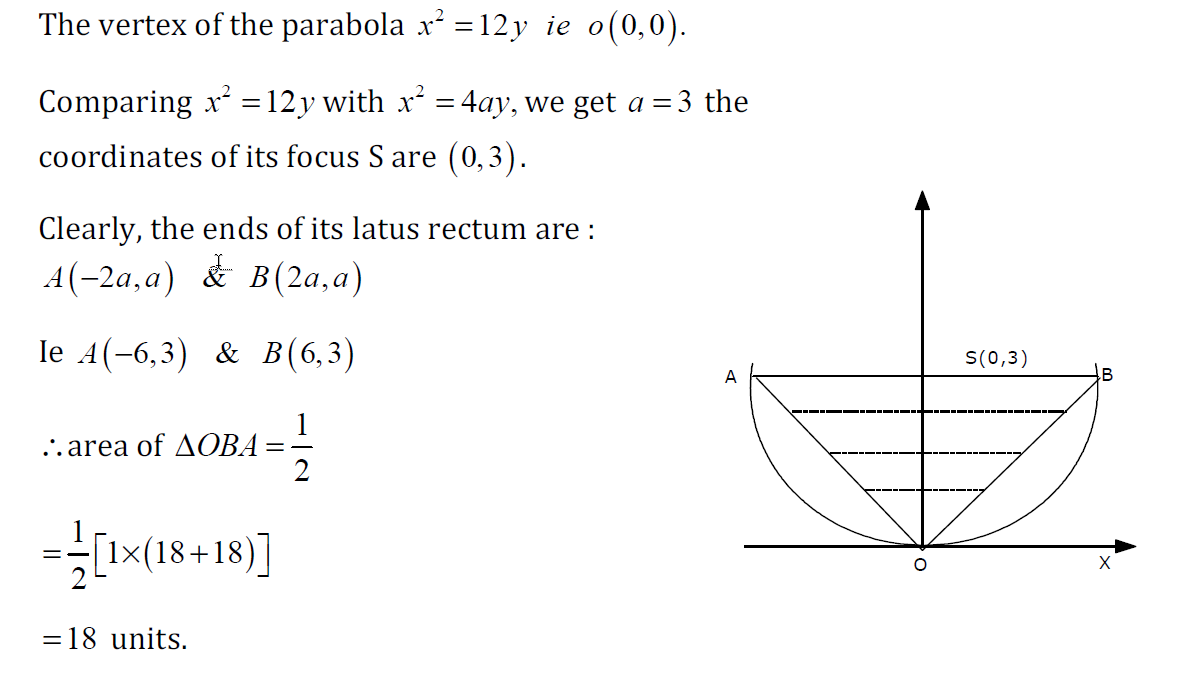
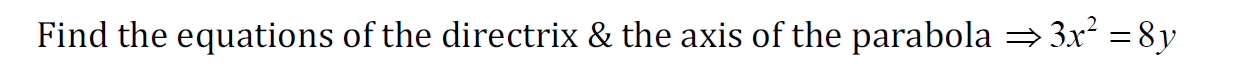Example 1
Sketch the parabola
y=x2/2
Find the focal length and indicate the focus and the directrix on your graph.
The focal length is found by equating the general expression for y
$y=x^2/(4p)$
and our particular example:
$y=x^2/2$
So we have:
$x^2/(4p)=x^2/2$
This gives $p = 0.5$.
So the focus will be at $(0, 0.5)$ and the directrix is the line $y = -0.5$.
Our curve is as follows:
Example 2
Sketch the curve and find the equation of the parabola with focus (−2,0) and directrix x = 2.
In this case, we have the following graph:
After sketching, we can see that the equation required is in the following form, since we have a horizontal axis:
$y^2 = 4px$
Since $p = -2$ (from the question), we can directly write the equation of the parabola:
$y^2 = -8x$
Example 3
Find the equation of the parabola having vertex (0, 0), axis along the x-axis and passing through (2, −1).The curve must have the following orientation, since we know it has horizontal axis and passes through $(2, -1)$:
So we need to use the general formula for a parabola with horizontal axis:
$y^2= 4px$
We need to find `p`. We know the curve goes through $(2, -1)$, so we substitute:
$(-1)^2= 4(p)(2) $
→ `1 = 8p`
→ $p = 1/8$.
So the required equation is $y^2=x/2$.
Example 4